
You have no idea why your left testicle hurts. It hurts more when you lift something or exercise. You may wonder if it’s something serious. Could it be cancer? What is going on?
Why Does My Left Testicle Hurt?
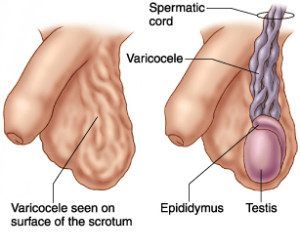
Often, a very common and treatable condition is what causes pain in the left testicle. It’s possible you have a condition known as varicocele. Varicocele is when veins in your scrotum don’t function correctly, which results in blood that pools in certain areas, instead of flowing like it should, through the body.[i] Typically, the dilated veins are in the spermatic cord within the scrotal sac.[ii] Varicocele has been linked to other problems like infertility and low testosterone levels.[iii]
What Causes Pain in the Left Testicle?
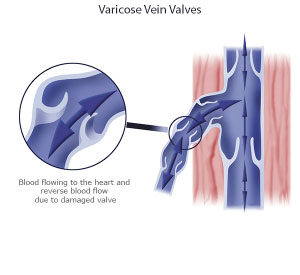 The majority of varicoceles – approximately 85% – occur on the left side.[ii] Why is this? The reason is because the veins on the left side of the scrotum and testicles are anatomically structured differently than the veins on the right are. Specifically, two arteries compress the left renal vein, which impedes blood coming into the vein from the spermatic vein. If the venous valves are dysfunctional, there is backpressure and the veins dilate, resulting in a varicocele.[ii]
The majority of varicoceles – approximately 85% – occur on the left side.[ii] Why is this? The reason is because the veins on the left side of the scrotum and testicles are anatomically structured differently than the veins on the right are. Specifically, two arteries compress the left renal vein, which impedes blood coming into the vein from the spermatic vein. If the venous valves are dysfunctional, there is backpressure and the veins dilate, resulting in a varicocele.[ii]
In comparison, veins on the right side have a straighter path. On the right side, the spermatic vein flows directly into the inferior vena cava, allowing for a more free-flowing path.[ii]
Is There Right Testicle Pain?
It is entirely possible to have varicocele on both sides, although it isn’t as common as having it on the left. Bilateral varicoceles can be slightly more difficult to treat. While surgery is an option for those with bilateral varicoceles, one drawback for many men is the post-surgical pain that can be ongoing for several days or even weeks.i Surgeries will have a longer recovery time than a minimally invasive treatment option like varicocele embolization — surgery can take up to 2 weeks to fully recover, versus a 1 – 2 day period for embolization.[i]
Is This a Sign of Something Serious?
Although varicocele can be painful, it typically isn’t something that’s considered serious, and the good news is the condition can be treated.[iv] Many men begin developing varicocele during puberty. In fact the overall incidence rate for adolescent boys is between 10 and 20%.[ii] However, if varicocele develops suddenly in older men, or if there is a mass, in very rare instances, this may indicate that there is a retroperitoneal tumor blocking the spermatic vein.[ii]
Typically, bilateral varicocele is identified with the enlarged right testicle remaining smaller in size than the left. The left side may be a grade 2 or 3 varicocele with the right side a grade 1.[v]
What Are My Treatment Options for Varicocele?
There are three basic surgical treatment options for varicocele and one minimally invasive option.
- Open Surgery: An incision is made into the abdomen to access and treat the dysfunctional veins.
- Microsurgery: The preferred surgical approach, due to its low complication and recurrence rate.
- Laparoscopic: The laparoscopic approach uses specialized robotic equipment to complete the surgery.[ii]
- Varicocele Embolization: For men seeking a less invasive technique to treat their varicocele, there is a non-surgical, minimally invasive treatment alternative known as varicocele embolization. In varicocele embolization, a small catheter is inserted, usually through the groin, to stop blood flow through the affected veins. The blood flow from the occluded veins is rerouted to other healthy veins to restore normal blood flow.[iii]
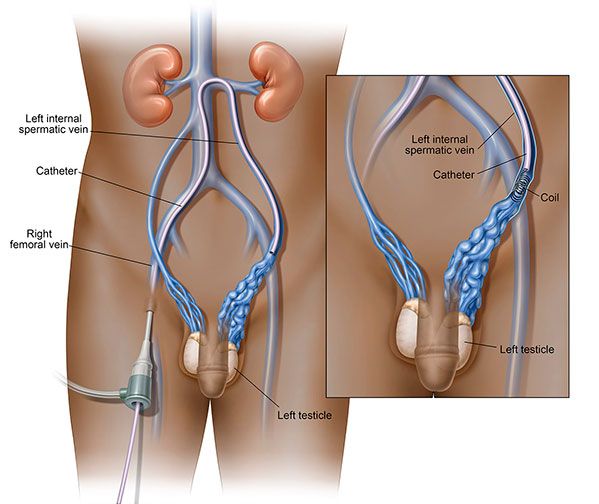
The Difference in Treatment Options
While embolization can be done on an outpatient basis, men who undergo a surgical procedure to treat their varicocele may be required to stay overnight in the hospital.[iii] Another difference is the actual time each procedure takes. An embolization procedure takes around 1 hour, but surgery takes around 4 hours.[vi] [vii] Recovery time for embolization is shorter as well, with many men returning to normal activities in 1 – 2 days, versus a 2 – 3 week period after surgery. Sexual activity is limited for 1 – 2 weeks for embolization patients, whereas surgical patients are advised to wait up to 4 weeks post procedure.[viii]
For those with bilateral varicocele, a huge advantage to embolization is that it allows men to have both sides repaired during the same procedure, through one puncture site.[iii] Men who choose surgery to repair bilateral varicocele can have both repaired at the same time, but will have two separate, open incisions.[iii]
Most often, varicocele treatment immediately ends pain in the testicles. Only your doctor can determine what may be causing your testicular pain, and if the diagnosis is varicocele, rest assured that it is a very treatable condition that in most cases doesn’t require surgery.
Sources:
[i] http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/varicocele/basics/definition/con-20024164
[ii] http://www.healthcommunities.com/varicocele/overview-of-varicocele.shtml

